The demand for efficient and sustainable energy storage solutions has surged recently. Among the various types of batteries available, lead-carbon batteries and zinc-carbon batteries have emerged as popular options. This article explores the differences between these two battery technologies, helping you determine which suits your needs better.
Part 1. What are lead carbon batteries?
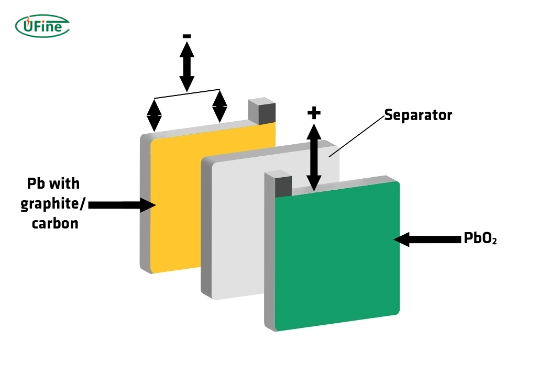
Lead carbon batteries represent a new generation of lead-acid batteries. These batteries enhance performance, longevity, and cycle life by incorporating carbon additives into the negative electrode. These enhancements make them suitable for various applications, from renewable energy storage to uninterruptible power supplies (UPS).
Key Features of Lead Carbon Batteries
- Improved Cycle Life: They can endure more charge-discharge cycles than traditional lead-acid batteries, often exceeding 3,000 cycles.
- Higher Charge Acceptance: This allows quicker recharging, making them ideal for applications requiring frequent cycling, such as solar energy systems.
- Enhanced Efficiency: Incorporating carbon improves energy conversion efficiency, improving performance under various load conditions.
- Temperature Resilience: Lead carbon batteries perform better in extreme temperatures than traditional lead-acid batteries, making them suitable for diverse environments.
Applications of Lead Carbon Batteries
Lead carbon batteries are increasingly being utilized in various applications due to their superior performance characteristics:
- Renewable Energy Systems include solar power storage systems where efficient energy management is critical.
- Electric Vehicles (EVs): Their longevity and quick charging capabilities make them suitable for EV applications where reliability is essential.
- Uninterruptible Power Supplies (UPS): They provide reliable backup power during outages, ensuring critical systems remain operational.
Emerging Applications
As technology evolves, lead-carbon batteries are being explored in new areas such as:
- Smart Grids: Their ability to handle variable loads makes them ideal for integration into innovative grid systems that require real-time energy management.
- Grid Energy Storage: They can store excess energy generated during peak production times for later use during high-demand periods.
Part 2. What are zinc-carbon batteries?
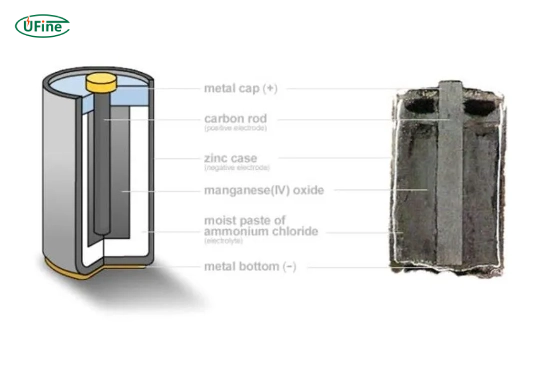
Zinc-carbon batteries are a type of dry cell primarily used for low-drain devices. They offer simplicity and cost-effectiveness, making them a standard household choice for powering remote controls, flashlights, and other low-energy devices.
Characteristics of Zinc-Carbon Batteries
These batteries have distinct characteristics:
- Affordability: Zinc-carbon batteries are generally cheaper than their counterparts, making them an attractive option for everyday use.
- Availability: They are widely available and can be found in nearly every convenience store, ensuring easy access for consumers.
- Limited Lifespan: Compared to other batteries, zinc-carbon batteries tend to have a shorter lifespan and are less suitable for high-drain devices.
- Lower Energy Density: Zinc-carbon batteries have lower energy density than lead-carbon batteries, meaning they store less energy relative to size.
Applications of Zinc-Carbon Batteries
Zinc-carbon batteries find their niche in low-drain applications:
- Household Devices: Commonly used in remote controls, clocks, and flashlights due to their affordability.
- Toys: Many battery-operated toys utilize zinc carbon because they provide sufficient power without high costs.
- Low-Power Electronics: Devices that do not require high energy output benefit from zinc-carbon’s affordability and availability.
Part 3. In-depth comparison of lead carbon and zinc-carbon batteries
Performance
- Lead Carbon batteries excel in various applications due to their enhanced cycle life and efficiency. They can endure numerous charge-discharge cycles—often exceeding 3,000 cycles—making them ideal for renewable energy systems and electric vehicles. Their ability to accept a fast charge means they can be recharged quickly, which is beneficial in high-demand situations.
- Zinc-Carbon Batteries: While zinc-carbon batteries are generally less efficient, they perform adequately for low-drain devices like remote controls and flashlights. However, they have a limited lifespan, typically lasting only 150 to 300 cycles. This makes them unsuitable for applications requiring frequent recharging or high energy output.
Environmental Impact
- Lead Carbon: These batteries are recyclable, but improper disposal can lead to lead contamination in soil and water, posing significant environmental risks. Responsible recycling practices are crucial to minimizing this impact.
- Zinc-Carbon: Zinc-carbon batteries can also be recycled; however, they can release zinc into the environment if not disposed of correctly. This leaching can affect local ecosystems and water sources.
Cost
- Lead-acid batteries: Although they have a higher initial price tag—typically ranging from $200 to $500—they offer long-term savings due to their durability and efficiency. Over time, the reduced need for replacements makes them cost-effective for many users.
- Zinc-Carbon Batteries: These batteries are much cheaper upfront, usually costing less than $5 per pack. However, their shorter lifespan means that users may spend more over time if they frequently need replacements.
Safety
- Lead Carbon is generally safe when handled properly; however, the presence of lead means that caution should be exercised during disposal to avoid environmental contamination.
- Zinc-Carbon: Considered safe for household use; these batteries do not pose significant risks under normal conditions. Nevertheless, improper disposal can lead to environmental hazards.
Overall Comparison Table
| Feature | Lead Carbon Batteries | Zinc-Carbon Batteries |
|---|---|---|
| Lifespan | 3,000+ cycles | 150 – 300 cycles |
| Efficiency | High | Moderate |
| Initial Cost | $200 – $500 | <$5 per pack |
| Environmental Impact | Recyclable but hazardous if improperly disposed | Recyclable but can leach zinc |
| Application Suitability | Renewable energy systems, EVs, UPS | Low-drain devices |
| Safety | Safe with proper handling | Generally safe |
Part 4. FAQs
-
What is the primary difference between lead-carbon and zinc-carbon batteries?
The main difference is their performance characteristics; lead-carbon batteries offer better durability and efficiency than zinc-carbon options. -
How long does a lead-carbon battery last compared to a zinc-carbon battery?
Lead-carbon batteries can last over a decade with proper care, while zinc-carbon batteries typically last only a few months under normal usage conditions. -
Are zinc-carbon batteries recyclable?
Yes, zinc-carbon batteries can be recycled; however, they must be disposed of properly to prevent environmental harm. -
Which battery is better for renewable energy systems?
Lead carbon batteries are generally more suitable for renewable energy systems due to their efficiency and longer lifespan than zinc-carbon alternatives. -
Can I use lead-carbon batteries in everyday devices?
Lead-carbon lead-carbon batteries may be better suited for high-drain applications. In contrast, zinc-carbon batteries are ideal for low-drain devices commonly found in households.
Related Tags:
More Articles

GoPro Battery Charger Guide: Top Picks & Pro Charging Tips
Explore the best GoPro chargers, compare third-party options, and learn how to charge smarter for longer battery life.
GoPro Battery Life Comparison: How Long Does a GoPro Battery Last?
Find out how GoPro battery life varies by model and get practical advice to maximize runtime for every adventure.
What Battery Powers Your GoPro?
Learn all about GoPro batteries - compatibility, runtime, charging tips, and how to extend battery life for longer shoots.
What Is a Disk Battery? A Simple Guide for Non-Tech Users
A disk battery is a small, round cell used in watches, remotes, and other electronic devices. It delivers steady power for compact, low-drain devices.
What Battery Powers a Space Heater?
Discover the type of battery that powers space heaters and learn how to choose the right one for efficient heating in your home or office.