- Part 1. Why lithium battery disposal is important
- Part 2. What are lithium batteries made of?
- Part 3. Why should lithium batteries not be placed in municipal or household recycling bins?
- Part 4. How do I identify which products contain lithium batteries?
- Part 5. What you should NOT do when disposing of lithium batteries
- Part 6. How to prepare lithium batteries for Disposal
- Part 7. Where to Dispose of Lithium Batteries
- Part 8. Specialized Battery Recyclers: What Do They Recover?
- Part 9. Storing Lithium Batteries When Not in Use
- Part 10. What About Industrial or EV Lithium Batteries?
- Part 11. Global and Local Regulations You Should Know
- Part 12. Conclusion: Recycle Right, Stay Safe
Lithium batteries power our everyday lives—from smartphones and laptops to electric scooters, power tools, and more. As their use grows, so does the need for safe disposal. Improperly discarding lithium batteries can cause fires, environmental harm, or even legal issues. So, how do you dispose of lithium batteries correctly?
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll walk you through everything you need to know: identifying lithium-ion batteries, understanding their components, preparing them for recycling, and where to take them for safe disposal. Let’s make battery recycling part of your routine.
Part 1. Why lithium battery disposal is important
Improper disposal of lithium batteries can be dangerous. Unlike alkaline batteries, lithium batteries contain volatile components that can catch fire or explode if damaged. Tossing them in the trash or regular recycling bin not only endangers sanitation workers but also risks contaminating soil and water.
More importantly, lithium batteries contain metals like cobalt, nickel, and lithium—critical materials that are non-renewable. Recycling ensures these valuable materials are reused, reducing the need for harmful mining operations.
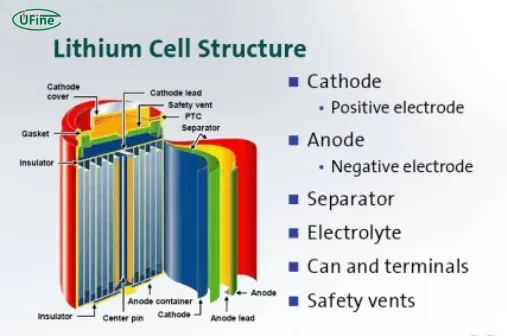
Part 2. What are lithium batteries made of?
Understanding the materials inside lithium batteries is key to knowing why they must be handled with care. Lithium-ion batteries typically contain:
- Lithium metal or lithium compounds
- Cobalt
- Nickel
- Manganese
- Graphite
- Electrolyte (flammable liquid)
- Plastic casing
- Copper and aluminum foils
Each of these materials has environmental and economic value. However, if discarded improperly, they can become hazardous.
Part 3. Why should lithium batteries not be placed in municipal or household recycling bins?
You might think tossing a used battery into your curbside recycling bin is helpful—but for lithium-ion batteries, it’s a serious mistake. Here’s why:
- Fire Hazard: If a battery gets punctured, crushed, or overheated in a garbage truck or recycling facility, it may spark and ignite.
- Chemical Leaks: Damaged batteries can leak toxic chemicals, contaminating local ecosystems.
- Not Designed for Batteries: Household recycling systems aren’t equipped to process hazardous electronics or recover battery materials safely.
Instead, lithium-ion batteries must go to certified battery recyclers or designated collection points.
Part 4. How do I identify which products contain lithium batteries?
You’d be surprised how many common items around your home or workplace contain lithium-ion batteries. Here’s how to identify them:
Common Products
- Smartphones, laptops, and tablets
- Power tools and cordless drills
- Electric bikes and scooters
- Portable power banks
- Bluetooth headphones
- Cameras and drones
- Smartwatches and fitness trackers
Identification Tips
- Look for labels that say “Li-ion” or “Lithium-ion”
- Check your device’s manual or battery compartment
- Many products display a battery symbol with recycling or caution markings
If the product is rechargeable, it likely contains a lithium-ion battery.
Part 5. What you should NOT do when disposing of lithium batteries
When asking “how do you dispose of lithium batteries,” it’s just as important to understand what not to do:
- Don’t throw them in the trash.
- Don’t place them in household recycling bins.
- Don’t incinerate or expose them to heat.
- Don’t puncture or crush the battery.
- Don’t store damaged or swollen batteries in closed containers.
These actions can lead to fires, environmental hazards, or physical harm.
Part 6. How to prepare lithium batteries for Disposal
Before recycling, you should always prepare lithium batteries to reduce the risk of accidents.
Safe Preparation Checklist
- Discharge the Battery (if safe to do so): Only for devices you can power on safely.
- Tape the Terminals: Use non-conductive tape (e.g., electrical tape) to cover battery terminals. This prevents accidental short-circuiting.
- Place in a Plastic Bag: Sealing each battery in a clear bag reduces risk during transport.
- Label if Damaged: If the battery is swollen, leaking, or damaged, label it clearly and notify the recycling center.
Proper preparation keeps both you and recycling workers safe.
Part 7. Where to Dispose of Lithium Batteries
You can’t throw lithium batteries in the trash—but there are plenty of safe options for recycling.
Drop-Off Locations
- Retail Stores: Big-box retailers like Home Depot, Staples, and Best Buy often accept rechargeable batteries.
- Local Recycling Centers: Many municipalities offer e-waste drop-off events or locations.
- Mail-In Programs: Services like Call2Recycle allow you to mail in used batteries safely.
Use websites like Earth911.com or Call2Recycle.org to find a certified collection point near you.
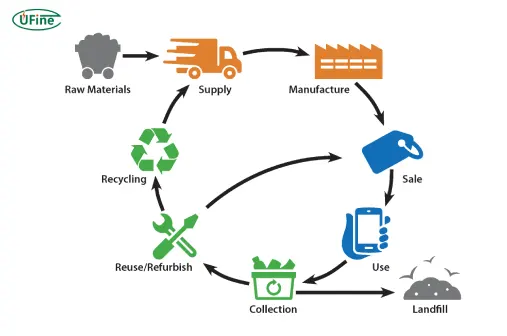
Part 8. Specialized Battery Recyclers: What Do They Recover?
Certified recyclers specialize in extracting valuable and reusable materials from lithium batteries. These include:
- Lithium
- Cobalt
- Nickel
- Copper
- Aluminum
- Graphite
Advanced recycling techniques reduce the need to mine raw materials, lower manufacturing costs, and protect ecosystems. Some companies even work toward closed-loop recycling, where recycled materials go directly into producing new batteries.
Part 9. Storing Lithium Batteries When Not in Use
If you’re not ready to recycle a battery immediately, storage is critical to avoid fire or leakage.
Storage Safety Tips
- Store in a cool, dry place.
- Keep away from flammable materials.
- Avoid high heat or direct sunlight.
- Use original packaging if possible.
- Tape terminals and isolate individual batteries.
Never store damaged or swollen batteries. Recycle those immediately through a certified hazardous waste program.
Part 10. What About Industrial or EV Lithium Batteries?
Larger lithium batteries used in electric vehicles (EVs), solar energy storage, or commercial equipment require special handling:
- Contact the manufacturer: Many companies have take-back or recycling programs.
- Use industrial recyclers: Certified facilities can handle large-scale or damaged battery systems.
- Never try to dismantle them yourself: High-voltage systems are extremely dangerous.
EV battery disposal is regulated in many regions due to its complexity and environmental risks.
Part 11. Global and Local Regulations You Should Know
Disposal regulations vary by location. However, most regions treat lithium batteries as hazardous waste and require special handling.
- United States: The EPA regulates battery disposal and supports programs like Call2Recycle.
- EU: Battery Directive mandates producer responsibility for battery recycling.
- Asia: Countries like China and Japan have growing lithium battery recycling infrastructure.
Always check with your local environmental agency for the latest rules and drop-off sites.
Part 12. Conclusion: Recycle Right, Stay Safe
So, how do you dispose of lithium batteries responsibly? It’s not difficult—just different. Proper disposal protects our environment, conserves valuable resources, and reduces the risk of fire or injury.
Here’s your quick action plan:
- Identify products with lithium-ion batteries.
- Never toss them in the trash or regular recycling bin.
- Prepare batteries safely using tape and bags.
- Use certified drop-off or mail-in programs.
- Store unused batteries carefully until recycling.
By taking just a few extra steps, you can make a big impact on the planet—and your safety.
Related Tags:
More Articles

What are Watts and Watt Hours in Battery?
Understand watt vs watt-hour in batteries, how to calculate battery watt hours, and what Wh means for car batteries, devices, and energy storage.
A Complete Guide to the Best Batteries for Flashlights
Compare the best batteries for flashlights, including AA, AAA, 18650, 21700, CR123A. See which battery offers the best brightness, runtime, and reliability.
How Long Do Rechargeable AA Batteries Last?
How long do rechargeable AA batteries last? Compare NiMH and lithium AA lifespan, recharge cycles, key factors, and performance vs alkaline batteries.
How Much Current Can a 9V Battery Really Supply?
Discover how many amps a 9V battery can supply, its actual current output, discharge rate, and capacity for alkaline, lithium, and rechargeable 9V batteries.
12V STD vs 12V AGM: Meaning, Differences, and Which Is Better
Understand what STD and AGM batteries mean, their key differences, and which 12V battery fits your needs best in 2026.