Lithium batteries power a wide range of devices, from smartphones to electric vehicles. Knowing how to connect these batteries in series, parallel, or even a combination, can help you tailor their performance to meet specific needs. In this article, we’ll explore the basics and provide detailed, step-by-step instructions on how to connect lithium batteries in series, parallel, and series-parallel configurations.
Here, we will take 3.7V 100mAh lithium cells as an example to explain in detail.
Part 1. Understanding batteries connecting in series
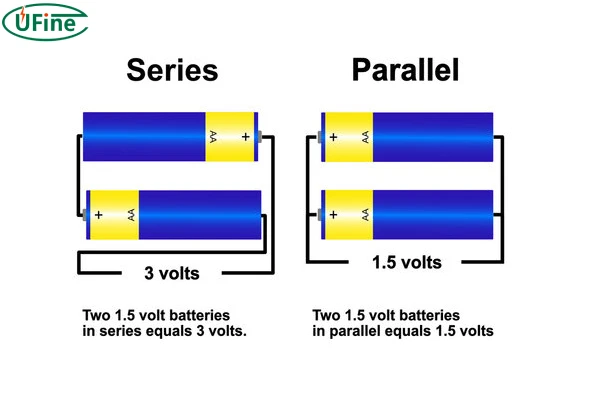
A series connection involves linking batteries end-to-end to increase the total voltage while keeping the same capacity (measured in milliampere-hours, or mAh). For example, connecting two 3.7V 100mAh lithium cells in series will yield a total voltage of 7.4V, but the capacity remains 100mAh. This type of connection is ideal when your device requires a higher voltage than a single battery can provide.
Characteristics of Series Connection:
- Voltage: Sum of individual voltages (e.g., 3.7V + 3.7V = 7.4V).
- Capacity: Remains the same (e.g., 100mAh).
- Usage: Suitable for devices requiring higher voltage.
Connecting Batteries in Series Pros:
- Increased Voltage: Connecting batteries in series adds their voltages together. This is ideal for devices or systems requiring higher voltage, such as certain power tools and vehicles.
- Simple Setup: It’s straightforward to connect batteries in series, making them easier to wire for high-voltage applications.
Connecting Batteries in Series Cons:
- No Increase in Capacity: While the voltage increases, the total capacity remains the same as a single battery. This may limit run time.
- Imbalance Risk: If one battery in the series is weaker or fails, it can affect the whole series, reducing performance or causing failure.
- Need for Matching Batteries: All batteries should be of the same type, voltage, and age. Otherwise, uneven charging/discharging can cause damage to the weaker battery.
Part 2. Understanding batteries connecting in parallel
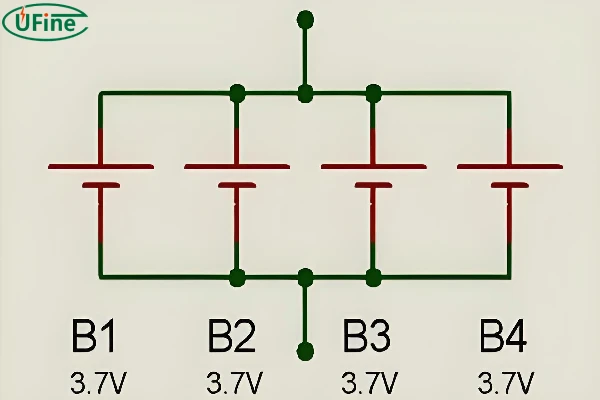
In a parallel connection, the batteries are linked side-by-side. This configuration keeps the voltage the same but increases the capacity. For instance, connecting two 3.7V 100mAh lithium cells in parallel will result in a total capacity of 200mAh while maintaining the voltage at 3.7V. This setup is beneficial when you need to extend the battery life of your device.
Characteristics of Parallel Connection:
- Voltage: Remains the same (e.g., 3.7V).
- Capacity: Sum of individual capacities (e.g., 100mAh + 100mAh = 200mAh).
- Usage: Ideal for devices that need longer battery life without changing voltage.
Connecting Batteries in Parallel Pros:
- Increased Capacity: When you connect batteries in parallel, their capacities (mAh or Ah) add up, providing longer battery life.
- Same Voltage: The voltage remains the same as a single battery, which can simplify compatibility with your device or system.
- Redundancy: If one battery fails, the others can still provide power, reducing the risk of a total power loss.
Connecting Batteries in Parallel Cons:
- Requires Same Battery Type: All batteries must have the same voltage, capacity, and age for balanced performance. Otherwise, weaker batteries can drain faster or fail early.
- Potential for Imbalance: If the batteries are not well-matched, charging and discharging may not be even, which can lead to inefficiency and damage over time.
- Complex Wiring: Setting up parallel connections can be tricky, especially if you’re connecting multiple batteries.
Part 3. Understanding batteries connecting in series-parallel
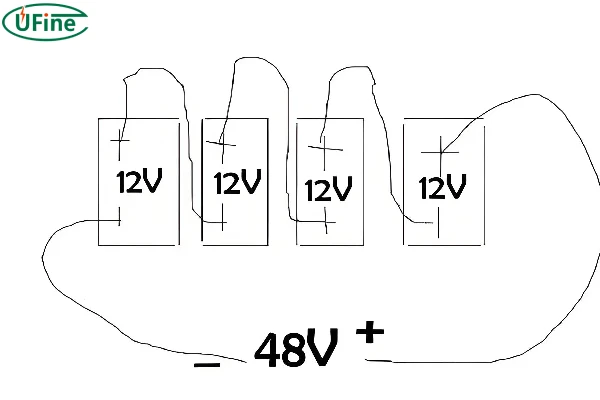
A series-parallel connection combines both configurations to increase both voltage and capacity. For example, connecting four 3.7V 100mAh lithium cells in a series-parallel setup (two sets of series connections linked in parallel) will give you 7.4V and 200mAh. This method is useful for applications that require higher voltage and extended battery life.
Characteristics of Series-Parallel Connection:
- Voltage: Combined voltage of series sets (e.g., 7.4V).
- Capacity: Combined capacity of parallel sets (e.g., 200mAh).
- Usage: Suitable for devices needing both higher voltage and longer battery life.
Batteries In Series Vs Parallel:Which Is Better?
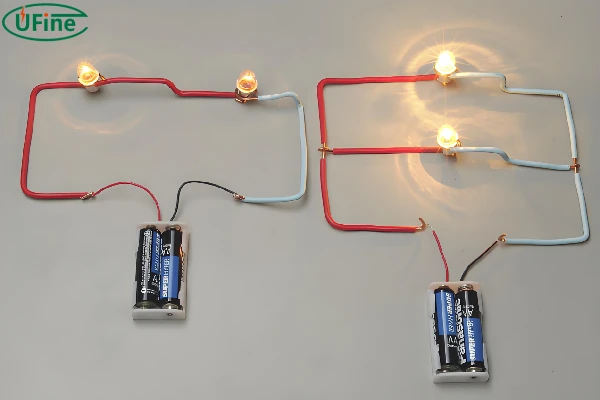
Part 4. How to connect lithium batteries in series?
- Gather Materials: Prepare 3.7V 100mAh lithium cells, connecting wires, a soldering iron, and safety gear.
- Identify Terminals: Locate the positive (+) and negative (-) terminals on each battery.
- Prepare the Batteries: Ensure that all batteries are of the same type and charge level to prevent imbalances.
- Connect in Series: Solder the positive terminal of the first battery to the negative terminal of the second battery. If you have more batteries, continue this pattern: positive to negative.
- Final Connection: The remaining free terminals (one positive and one negative) become the output terminals for your series connection
- Check Connections: Use a multimeter to verify the total voltage and ensure all connections are secure.
By following these steps, you can safely connect your lithium batteries in series, increasing the overall voltage while maintaining the same capacity.
Part 5. How to connect lithium batteries in parallel?
- Gather Materials: Prepare your 3.7V 100mAh lithium cells, connecting wires, a soldering iron, and safety gear.
- Identify Terminals: Locate the positive (+) and negative (-) terminals on each battery.
- Prepare the Batteries: Make sure all batteries are identical and equally charged.
- Connect in Parallel: Solder all the positive terminals together using a wire. Solder all the negative terminals together with another wire.
- Final Connection: The combined positive terminals and combined negative terminals serve as the output terminals for your parallel connection.
- Check Connections: Use a multimeter to verify the total capacity and ensure all connections are secure.
This parallel setup will keep the voltage the same but significantly increase the capacity, allowing for a longer runtime for your devices.
Complete Overview Lithium Batteries in Parallel and Series
Part 6. How to connect lithium batteries in series and parallel?
- Gather Materials: You will need four 3.7V 100mAh lithium cells, connecting wires, a soldering iron, and safety gear.
- Identify Terminals: Locate the positive (+) and negative (-) terminals on each battery.
- Prepare the Batteries: Ensure all batteries are of the same type and charge level.
- Create Series Pairs: Connect two batteries in series by soldering the positive terminal of the first battery to the negative terminal of the second battery. Do the same for the other two batteries.
- Combine Series Pairs in Parallel: Solder the positive terminals of both series pairs together using a wire. Solder the negative terminals of both series pairs together with another wire.
- Final Connection: The combined positive terminals and combined negative terminals serve as the output terminals for your series-parallel connection.
- Check Connections: Use a multimeter to verify the combined voltage and capacity and ensure all connections are secure.
This method increases both the voltage and the capacity of your battery pack, making it suitable for devices that require both higher voltage and extended battery life.
Part 7. Which method should you choose to connect lithium cells?
When to Connect Lithium Batteries in Series?
You should connect lithium batteries in series when your device requires a higher voltage than a single battery can provide. For example, if your device operates at 7.4V, connecting two 3.7V batteries in series would be appropriate. This setup is commonly used in applications like electric scooters, drones, or other high-voltage devices.
When to Connect Lithium Batteries in Parallel?
A parallel connection is ideal when you need to extend your device’s battery life without changing the voltage. This is particularly useful for devices that require a longer runtime, such as portable speakers, power banks, or handheld devices. By increasing the total capacity, you can ensure your device runs longer between charges.
When to Connect Lithium Batteries in Series and Parallel?
Opt for a series-parallel connection when your device requires higher voltage and extended battery life. This configuration is useful in more complex applications like electric bicycles, solar power storage systems, and other high-power devices that benefit from increased voltage and capacity. This setup provides a balanced solution for demanding applications.
Following this comprehensive guide, you can effectively connect lithium batteries in series, parallel, or a combination of both to suit your specific needs. Whether you’re powering a small or large gadget, understanding how to properly connect your batteries will ensure optimal performance and longevity.
Part 8. Connecting battery tips
- Match Battery Types: Always use batteries of the same chemistry, capacity, and age to ensure safe and efficient performance.
- Balance the Batteries: When connecting multiple batteries in series or parallel, balance the charge levels before connecting them to avoid overcharging or deep discharging.
- Use a Battery Management System (BMS): A BMS helps monitor voltage, temperature, and charge levels, preventing overcharging or undercharging and extending battery life.
- Avoid Mixing New and Old Batteries: Using old batteries alongside new ones can cause the new batteries to discharge faster, leading to uneven wear.
- Check for Correct Voltage and Amp Rating: Always ensure the total voltage and amperage matches the requirements of your device or system.
- Use Quality Connectors and Wires: Ensure you use reliable connectors and wires to prevent overheating, voltage drops, and short circuits.
Part 9. FAQs
-
How does the internal resistance change when batteries are connected in parallel?
The total internal resistance of the parallel battery system decreases compared to a single battery. This allows for higher current delivery and better load sharing between the batteries. -
What are the key considerations for balancing charging in a parallel battery bank?
Ensuring all batteries have the same state-of-charge, capacity, and internal resistance is crucial for maintaining balanced charging. This often requires individual battery monitoring and charging control. -
What are the benefits and drawbacks of using fuses or circuit breakers in a parallel battery bank?
Fuses/breakers can isolate a failed battery and prevent it from affecting the others, but they add resistance and complexity to the system. -
How does the depth of discharge (DOD) affect the longevity of batteries in a parallel configuration?
Maintaining a higher state-of-charge and shallow DOD can help extend the service life of batteries connected in parallel, as this reduces the strain on individual cells. -
What challenges arise when connecting batteries with different capacities or states-of-charge in series?
Imbalances can lead to overcharging or overdischarging of individual batteries, which can damage them over time. Careful cell-level monitoring and balancing is required. -
How does the internal resistance impact the series battery bank?
Higher total internal resistance in a series configuration can result in greater voltage drops, heat generation, and energy losses compared to a parallel arrangement.
Related Tags:
More Articles

Safe Charging Protocols for Your 11.1V LiPo Battery Charger
Safely charge your 11.1V LiPo battery by following proper rates, using safety tools, and avoiding common charging mistakes.
11.1 V LiPo Battery Airsoft: Boosting Field Performance
Upgrade your airsoft gun with an 11.1V LiPo battery for faster firing, longer runtime, and top-tier performance on the battlefield.
Batteries for Trolling Motors Lightweight vs. Leaf Blower Power
Explore the best lightweight trolling motor batteries and how they compare to leaf blower power for performance, portability, and runtime.
What Is a 2C Battery?
Learn what a 2C battery is, how C-rates affect performance, and how to calculate the number of batteries your device needs.
What Battery Does LED Strips Use?
Discover which batteries power LED strips best. Learn about voltage, capacity, battery types, and how to safely power your LED lighting projects.