When choosing a deep cycle battery, weight is an important consideration. Whether you’re looking for a battery for your RV, boat, or solar system, knowing how much a deep cycle battery weighs can help you make a more informed decision. But why does the weight matter, and how does it impact performance? In this article, we’ll explore the factors affecting the weight of deep cycle batteries, compare different types, and offer guidance on how to choose the right battery for your needs.
Part 1. Why is the weight of deep cycle battery different?
Deep cycle batteries are designed to provide sustained power over a longer period, which makes them heavier than regular batteries. The materials used in their construction, such as thick plates and electrolytes, are more robust, allowing for deeper discharge and longer cycles. Unlike starter batteries, which only need a short burst of power, deep cycle batteries are built for longevity and endurance, which requires more durable, and consequently, heavier components.
For example, a typical deep cycle battery contains thicker lead plates than a standard car battery, contributing to the extra weight. The construction is intended to handle repeated charging and discharging, making it essential for applications like marine, RVs, and off-grid solar systems.
Part 2. How does weight affect the performance of deep cycle battery?
Weight plays a significant role in battery performance. A heavier deep cycle battery often indicates more capacity, which means it can store more energy and power your devices for longer.
- More Capacity: Heavier batteries typically offer higher amp-hour (Ah) ratings, meaning they can last longer between charges.
- Durability: A heavier battery is often more durable and better suited for high-demand applications. For instance, a 100Ah deep cycle battery weighs more than a 50Ah one, but it will last longer under heavy usage.
However, weight can also be a downside if portability is important. For example, if you need to carry the battery frequently, such as when using it for camping or in a mobile home, a heavier battery could become cumbersome. This is where the balance between weight and performance becomes essential.
Part 3. What affects the weight of deep cycle battery?
Several factors influence the weight of deep cycle batteries:
- Battery Chemistry: Different chemical compositions, such as lead-acid, lithium-ion, and AGM (Absorbed Glass Mat), result in varying battery weights. For example, lead-acid batteries tend to be heavier due to the lead plates, while lithium-ion batteries are lighter.
- Capacity: Higher capacity batteries have more materials inside them, leading to increased weight. A 200Ah battery will be heavier than a 100Ah battery of the same chemistry.
- Size and Design: Larger batteries with more cells and thicker plates will naturally weigh more. For example, batteries designed for solar power systems may be bigger and heavier to provide long-lasting energy storage.
- Construction Materials: The materials used for the casing and internal components can add to the battery’s weight. Some battery cases are designed to be more rugged and durable, adding to the overall mass.
Part 4. What are the weight differences of different types of deep cycle battery?
AGM VS Lithium VS Lead-Acid Battery: Comprehensive Comparison
Battery chemistry has a significant impact on the weight of deep cycle batteries. Let’s look at the weight differences among the common types:
Lead-Acid Batteries
These are the most traditional deep cycle batteries and are known for their affordability. However, they are quite heavy. A typical 12V, 100Ah lead-acid battery weighs around 60-70 pounds.
AGM (Absorbed Glass Mat) Batteries
AGM batteries, which are a type of lead-acid battery, are slightly lighter due to their sealed design. A 12V, 100Ah AGM battery weighs around 60 pounds but is often more durable and requires less maintenance.
Lithium-Ion Batteries
Lithium-ion batteries are much lighter compared to their lead-acid counterparts. A 12V, 100Ah lithium-ion battery may weigh as little as 30 pounds. The lighter weight, along with a longer lifespan and faster charging times, makes lithium-ion an increasingly popular option despite the higher cost.
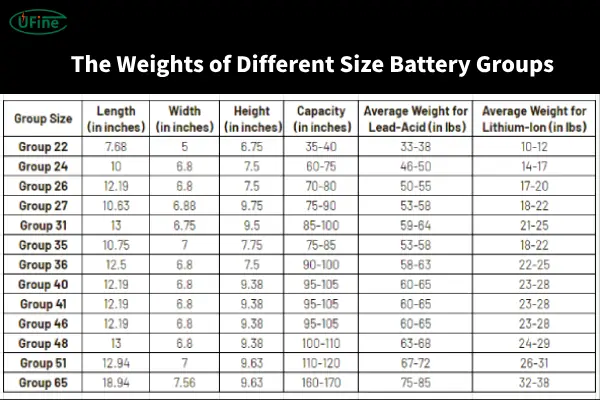
Part 5. What are the weights of different size battery groups?
Deep cycle batteries come in various group sizes, which also affect their weight. Common group sizes include Group 24, Group 27, and Group 31. Below is a comparison of weights based on these group sizes:
Part 6. How to choose between weight, performance, and cost?
When selecting a deep cycle battery, you need to balance weight, performance, and cost. Heavier batteries may provide better performance, but they can be more challenging to transport and install. Here’s how to approach the decision:
-
If performance is your priority: Choose a higher-capacity, heavier battery, especially for demanding applications like off-grid power storage or RVs.
-
If portability is essential: Lithium-ion batteries offer a good balance of performance and weight, making them ideal for mobile or portable use, despite their higher cost.
-
On a budget: Traditional lead-acid batteries are the most cost-effective, but you’ll have to deal with more weight and maintenance over time.
Part 7. Will a fully charged deep cycle battery be heavier?
A common question is whether a fully charged battery weighs more than a discharged one. In theory, the mass of the electrons flowing in and out during charging is so small that it doesn’t affect the weight in any measurable way. Thus, whether the battery is fully charged or not will not significantly change its weight.
However, the difference lies in its energy content, not its physical mass.
Part 8. Is it better for deep cycle batteries to be heavier or lighter?
The answer to this question depends on your needs. Heavier deep cycle batteries, like lead-acid or AGM types, tend to offer more capacity and durability. If you’re powering something that requires a lot of energy for an extended period, like a solar energy system, a heavier battery may be better because of its ability to hold more charge.
However, lighter batteries, such as lithium-ion, have their advantages too. They are easier to transport and install, and while they may cost more upfront, their longer lifespan and faster charging times can make them more economical in the long run.
Part 9. Conclusion
The weight of a deep cycle battery can significantly impact its performance, portability, and cost. Heavier batteries, like lead-acid, tend to provide more capacity, while lighter options, like lithium-ion, offer ease of use and longer lifespans. When choosing the right battery, consider your specific needs, including the amount of power you need, how often you need to move the battery, and your budget. Ultimately, the balance between weight, performance, and cost will determine the best battery for you.
Related Tags:
More Articles

LiPo Battery Discharge Rate Guide & Calculation Tips
Understand LiPo battery discharge rates, C-ratings, and how to calculate max current. Essential guide for RC, drones, and electronics users.
High‑Capacity 3S LiPo Batteries: 5000 mAh vs. 10000 mAh
Compare 3S LiPo 5000mAh vs 10000mAh batteries by weight, power, and use. Find the best fit for your drone, RC car, or boat setup.
Top 5 Applications for Small 3S LiPo Batteries
Small 3S LiPo batteries power drones, RC gear, wearables, and robotics with high energy and low weight. Making them ideal for compact electronics projects.
Building and Charging Your Own 3S LiPo Pack: A Step‑by‑Step Guide
Learn how to build, balance, and charge a 3S LiPo battery pack safely at home with this complete DIY guide for hobbyists and beginners.
How to Choose the Right LiPo Battery Plug Type?
Discover the best LiPo battery plug types, how to choose them, and expert tips for safe usage, soldering, and maintenance.