When understanding how many volts a car battery is, it’s essential to know that most standard car batteries operate at 12 volts. This voltage is crucial for starting the engine and powering the vehicle’s electrical systems. In this article, we will explore the voltage of car batteries in detail, including how they work, why their voltage matters, and the differences between traditional lead-acid batteries and newer lithium batteries.
Part 1. What is a car battery?
A car battery serves as the heart of your vehicle’s electrical system. It stores electrical energy and provides the necessary power to start the engine and run various electrical components. The most common type of car battery is the lead-acid battery, which uses lead dioxide and sponge lead plates submerged in an electrolyte solution of sulfuric acid.
Lithium batteries have also gained popularity recently, especially in electric vehicles (EVs). These batteries offer several advantages over traditional lead-acid batteries, such as higher energy density, longer lifespan, and faster charging times.
Key Functions of a Car Battery
- Starting the Engine: A car battery’s primary role is to deliver the high burst of energy needed to start the engine. This process requires significant power, which is why a fully charged battery is vital.
- Powering Electrical Systems: When your vehicle is off, the battery powers essential electrical components like lights, radio, and dashboard instruments. This ensures you can use these features even when the engine isn’t running.
- Stabilizing Voltage: The battery helps stabilize voltage levels in the electrical system. This stability ensures that all components receive consistent power, essential for proper functioning.
Part 2. How does voltage work in a car battery?
Voltage represents the electrical pressure that pushes current through a circuit. In a car battery, chemical reactions within its cells generate this pressure.
Understanding Voltage Levels
- Resting Voltage: When not used, a healthy car battery should have a resting voltage of around 12.6 volts or higher. This indicates that the battery is fully charged.
- Running Voltage: When the engine is running, the alternator takes over and charges the battery while also powering the vehicle’s electrical systems. The voltage can rise to between 13.5 to 14.5 volts during this time.
Part 3. How does the voltage of a car battery change when it’s running versus when it’s not?
The voltage levels in a car battery fluctuate depending on whether the engine is running.
- When Not Running: A fully charged car battery at rest will show about 12.6 volts or more. If it drops below 12 volts, it indicates that the battery may be weak or discharged.
- When Running: Once you start your vehicle, the alternator generates electricity to recharge the battery and power electrical systems. During this time, you can expect voltage readings between 13.5 and 14.5 volts as it compensates for any power in use.
This difference in voltage levels highlights how critical it is for your vehicle’s electrical system to have a properly functioning alternator and battery.
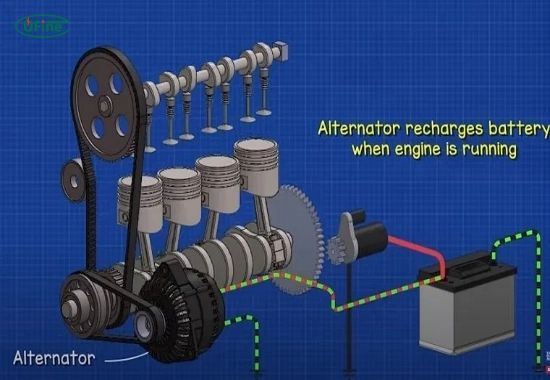
Part 4. How does the alternator affect the voltage of a car battery?
The alternator plays a significant role in maintaining your car battery’s voltage while driving.
- Charging Function: As you drive, the alternator generates electricity by converting mechanical energy from the engine into electrical energy. This process keeps your battery charged and ensures all electrical components function correctly.
- Voltage Regulation: The alternator also regulates voltage levels to prevent the battery from overcharging or undercharging. It typically maintains output within the ideal range of 13.5 to 14.5 volts, ensuring the battery stays healthy and prolongs its lifespan.
If your alternator fails, it can lead to insufficient battery charging, resulting in low voltage levels that can cause starting problems or other electrical issues.
Part 5. What is considered a healthy voltage for a car battery?
Understanding healthy voltage levels is essential for determining whether your car battery is functioning correctly.
Voltage Chart for Car Batteries
| Voltage Level | Battery Charge State |
|---|---|
| 12.6 volts or higher | 100% (Fully Charged) |
| 12.4 volts | 75% |
| 12.2 volts | 50% |
| 12.0 volts | 25% |
| Below 12.0 volts | Needs Charging |
| Below 11.8 volts | Weak or Dead |
When not used, a healthy car battery should maintain a resting voltage of at least 12.4 volts.
Part 6. Why does voltage matter?
The voltage of your car battery directly affects its performance and longevity:
- Engine Starting: If the voltage drops below 12 volts, your vehicle may struggle to start or fail.
- Battery Life: Consistently low voltage can lead to sulfation, damaging lead plates inside the battery and shortening its lifespan.
- Electrical System Performance: Insufficient voltage can cause erratic behavior in electrical components, leading to issues like dimming lights or malfunctioning electronics.
Part 7. Common causes of low car battery voltage
Understanding why your car’s battery might have low voltage can help prevent future issues:
- Age of Battery: Batteries typically last between three to five years; older batteries are more prone to failure.
- Frequent Short Trips: Short drives need to allow more time for the alternator to recharge the battery fully.
- Extreme Temperatures: Both hot and cold weather can affect a battery’s performance and lifespan.
Part 8. How to test your car battery’s voltage?
Testing your car battery’s voltage is straightforward and requires minimal tools:
Steps to Test Battery Voltage
1. Gather Tools: You will need a multimeter or voltmeter.
2. Turn Off Your Car: Ensure you turn off your vehicle before testing.
Connect Multimeter Leads:
- Attach the red lead to the positive terminal of the battery.
- Attach the black lead to the negative terminal.
3. Read Voltage: Check the multimeter display for the voltage reading.
4. Interpret Results:
- A reading of 12.6 volts or higher indicates a fully charged battery.
- A reading between 12.4 and 12.6 volts suggests adequate charge but may need attention soon.
- A reading below 12 volts indicates that charging is required.
Part 9. FAQs
-
How many volts does a new car battery have?
A new car battery typically has an initial resting voltage of around 12.7 volts, but it may settle at approximately 12.4 to 12.6 volts after being installed and used briefly. -
Can I drive with low voltage on my car battery?
Driving with low voltage can be risky; it may cause starting issues and affect other electrical components in your vehicle. -
How often should I check my car battery’s voltage?
It’s advisable to check your car’s battery voltage at least once every few months or before long trips. -
What happens if my car battery drops below 10 volts?
If your car’s battery drops below 10 volts, it’s generally considered dead or severely discharged and may not start your vehicle without assistance. -
Can I replace my car battery?
Yes, replacing your car battery is feasible if you follow safety precautions and have essential tools; however, consult your vehicle’s manual for specific instructions for your model.
Related Tags:
More Articles

LiPo Battery Discharge Rate Guide & Calculation Tips
Understand LiPo battery discharge rates, C-ratings, and how to calculate max current. Essential guide for RC, drones, and electronics users.
High‑Capacity 3S LiPo Batteries: 5000 mAh vs. 10000 mAh
Compare 3S LiPo 5000mAh vs 10000mAh batteries by weight, power, and use. Find the best fit for your drone, RC car, or boat setup.
Top 5 Applications for Small 3S LiPo Batteries
Small 3S LiPo batteries power drones, RC gear, wearables, and robotics with high energy and low weight. Making them ideal for compact electronics projects.
Building and Charging Your Own 3S LiPo Pack: A Step‑by‑Step Guide
Learn how to build, balance, and charge a 3S LiPo battery pack safely at home with this complete DIY guide for hobbyists and beginners.
How to Choose the Right LiPo Battery Plug Type?
Discover the best LiPo battery plug types, how to choose them, and expert tips for safe usage, soldering, and maintenance.