- Key Takeaways (Quick Summary)
- Part 1. What is battery memory effect? Causes vs myths
- Part 2. Do lithium-ion batteries have a memory effect? (technical explanation)
- Part 3. Why lithium batteries behave differently from NiCd & NiMH
- Part 4. What causes "memory-like" symptoms in lithium batteries
- Part 5. How memory-like issues affect battery performance
- Part 6. How to maximize lithium-ion battery lifespan (engineer-recommended)
- Part 7. Preventing battery memory myths in real applications
- Part 8. FAQs about battery memory effect
Do Lithium Batteries Have Memory? The Short Answer
No — lithium-ion batteries do not experience a true memory effect. Unlike older nickel-based chemistries, lithium-ion cells do not “remember” partial charge levels in a way that permanently reduces usable capacity.
However, improper usage patterns can create symptoms that look like memory effect, leading to confusion among users and engineers alike:
- 🔋 Repeated shallow charge cycles can cause voltage depression, reducing usable runtime
- 🌡️ High operating or charging temperatures accelerate irreversible capacity degradation
- ⚡ Battery management systems (BMS) may misreport state-of-charge after long-term partial cycling
Key Takeaways (Quick Summary)
- Lithium-ion batteries do not suffer true memory effect like NiCd batteries
- Capacity loss in lithium batteries is mainly caused by heat, aging, and voltage stress, not charging habits alone
- Partial charging is safe and recommended for daily lithium-ion use
- Occasional full charge–discharge cycles help recalibrate the BMS, not the chemistry
- Most “memory effect” complaints are actually voltage depression or capacity fade
- Proper temperature control has a greater impact on lifespan than charge depth
Part 1. What is battery memory effect? Causes vs myths
When users search “do lithium batteries have memory” or “lithium ion battery memory effect”, the term is often misapplied.
1 True memory effect (nickel-based batteries)
The true memory effect is a chemical phenomenon observed primarily in Nickel-Cadmium (NiCd) batteries:
- Repeated partial discharges lead to cadmium crystal growth
- The battery “locks in” a reduced capacity window
- Full capacity becomes inaccessible unless conditioned
2 Why the myth persists for lithium batteries
Lithium-ion batteries degrade differently:
- ❌ No crystalline memory formation
- ⚠️ Apparent capacity loss often caused by voltage depression or BMS miscalibration
- 🌡️ Heat-related aging is frequently mistaken for memory effect
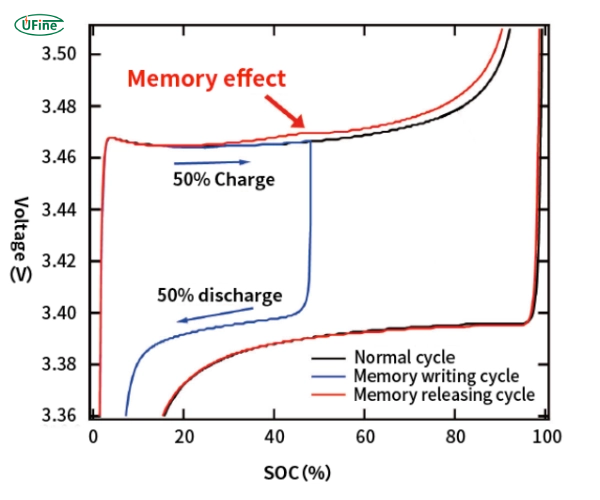
Part 2. Do lithium-ion batteries have a memory effect? (technical explanation)
1 Short technical answer
No. Lithium-ion battery memory effect does not exist at the electrochemical level.
2 What actually happens instead
| Issue | What It Is | Often Miscalled “Memory Effect”? |
|---|---|---|
| Voltage depression | Reduced operating voltage range after shallow cycling | ✅ Yes |
| Capacity fade | Loss of active lithium due to aging | ✅ Yes |
| BMS miscalibration | Inaccurate state-of-charge estimation | ✅ Yes |
| True memory effect | Crystal growth locking capacity | ❌ No |
Lithium-ion degradation is governed by:
- Solid electrolyte interphase (SEI) growth
- Lithium plating (under stress conditions)
- Cathode structural fatigue
For correct charging fundamentals, see: 👉 How to Charge a Lithium-ion Battery
Part 3. Why lithium batteries behave differently from NiCd & NiMH
1 Battery chemistry comparison
| Battery Type | True Memory Effect | Practical Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Nickel-Cadmium (NiCd) | ✅ Severe | Requires full discharge cycles |
| Nickel-Metal Hydride (NiMH) | ⚠️ Mild | Occasional conditioning needed |
| Lead-Acid | ❌ No | Sulfation mimics memory |
| Lithium-ion | ❌ None | Heat & voltage are dominant factors |
Lithium-ion cells maintain capacity independently of charge depth, which is why partial charging is widely recommended.
Part 4. What causes “memory-like” symptoms in lithium batteries
1 Repeated shallow cycling
Does not damage chemistry, but can confuse fuel-gauge algorithms.
2 High temperature exposure
The single biggest lifespan killer for lithium batteries.
- 35 °C accelerates SEI growth
- 45 °C causes rapid permanent capacity loss
3 Overcharging or deep discharging
Modern BMS reduces risk, but prolonged stress still degrades electrodes.
Part 5. How memory-like issues affect battery performance
- Shorter runtime per charge
- Earlier low-battery warnings
- Faster apparent drain at high SOC
- Increased heat generation under load
These effects are not reversible chemical memory, but in some cases BMS recalibration can restore reported capacity.
Part 6. How to maximize lithium-ion battery lifespan (engineer-recommended)
- Operate between 20–80% SOC for daily use
- Avoid charging above 35 °C (95 °F)
- Use certified chargers with correct voltage limits
- Store long-term at ~50% SOC
- Perform one full cycle every 1–2 months (calibration only)
- Avoid deep discharge below 5%
- Keep firmware updated for optimized charging algorithms
- Monitor battery health, not just cycle count
Part 7. Preventing battery memory myths in real applications
Lithium-ion batteries benefit more from thermal management and voltage moderation than from strict charging rituals. Unlike NiCd batteries, forcing full discharges frequently can actually shorten lithium battery lifespan.
Part 8. FAQs about battery memory effect
Do lithium-ion batteries need full discharge to prevent memory effect?
No. Full discharges are unnecessary and increase wear. Occasional full cycles are only for BMS calibration.
Can lithium batteries develop permanent memory effect?
No. Lithium-ion batteries do not chemically lock capacity like NiCd cells.
Why does my lithium battery seem to lose capacity after partial charging?
This is usually voltage depression or SOC miscalibration, not true capacity loss.
Does fast charging or wireless charging cause memory effect?
No, but excess heat from fast or wireless charging can accelerate degradation.
Are EV lithium batteries affected by memory effect?
No. EV packs use advanced BMS and thermal control; charging limits are set for longevity, not memory prevention.
Related Tags:
More Articles

Lead Acid vs. Lithium Ion Batteries: A Complete Comparison
Compare lead acid vs lithium-ion batteries in safety, cost per kWh, energy density, size, lifespan, and applications. Selection guide for engineers and buyers.
Learn how to charge a drone battery correctly. This guide covers battery types, chargers, safe charging steps, and best practices to extend battery life.
Capacitor vs Battery: What is the Difference?
Capacitor vs battery explained in detail. Learn the difference between capacitor and battery in energy storage, charging speed, lifespan, and real applications.
18650 Battery vs AA: Which Is Better for Your Device?
Compare 18650 vs AA batteries in capacity, voltage, rechargeability, and applications. Learn which battery type fits high-drain or everyday devices.
What is the Difference Between Battery Cell, Battery Control Module, and Battery Pack?
Compare battery cells, modules, and packs. Learn functions, design differences, control modules, and selection tips for EV, ESS, and industrial use.