When powering our modern world, secondary batteries play a vital role. From electric vehicles to portable electronics, these rechargeable power sources are omnipresent. This comprehensive guide will delve deep into secondary batteries, exploring their types, applications, advantages, and more. Whether you’re a tech enthusiast, an industry professional, or just curious about how these batteries work, this guide has something for you.
Part 1. What are secondary batteries?
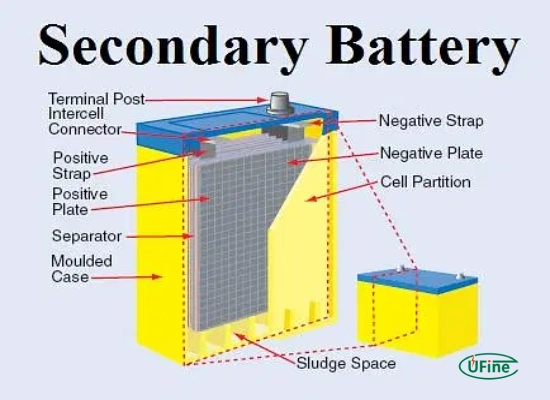
Secondary batteries, often called rechargeable batteries, are electrochemical cells that can be recharged and reused multiple times. Unlike primary batteries, which are designed for single use, secondary batteries can undergo numerous charge and discharge cycles. This makes them more sustainable and cost-effective in the long run.
Advantages of Secondary Batteries
1. Cost-Effectiveness
While the initial cost of secondary batteries can be high, their ability to be recharged and reused makes them more economical over time than primary batteries.
2. Environmental Benefits
Secondary batteries contribute to reducing waste and conserving resources. They also support using renewable energy sources to help mitigate climate change.
3. High Performance
Modern secondary batteries offer high energy densities, long cycle lives, and fast charging capabilities, meeting the demands of various high-performance applications.
Challenges and Limitations of Secondary Batteries
1. Safety Concerns
Safety is a significant concern, especially with Li-ion batteries. If not adequately managed, issues like thermal runaway and overheating can lead to fires and explosions.
2. Environmental Impact
Despite their benefits, the production and disposal of secondary batteries pose environmental challenges. Proper recycling and disposal methods are essential to mitigate these impacts.
3. Cost and Availability
The materials used in high-performance batteries, such as lithium and cobalt, can be expensive and subject to supply chain constraints.
The Difference Between Primary and Secondary Battery
Part 2. The history of secondary batteries
Early Innovations
The journey of secondary batteries began in the 19th century. The first successful secondary battery was the lead-acid battery, invented by French physicist Gaston Planté in 1859. This invention laid the groundwork for future developments in rechargeable battery technology.
Modern Developments
Fast forward to the late 20th and early 21st centuries, and we witness the advent of nickel-cadmium (NiCd), nickel-metal hydride (NiMH), and lithium-ion (Li-ion) batteries. These innovations significantly improved energy density, cycle life, and safety.
Part 3. Types of secondary batteries
Lithium-Ion (Li-ion) Batteries
Li-ion batteries are the gold standard in today’s rechargeable battery market. They are used in everything from smartphones to electric vehicles due to their high energy density and long cycle life.
Advantages
- High energy density
- Long lifespan
- Lightweight
Disadvantages
- Expensive to produce
- Safety concerns, particularly with overheating
Lead-Acid Batteries
Lead-acid batteries are the oldest type of rechargeable battery and are still widely used today. They are known for their reliability and ability to deliver high surge currents, making them ideal for automotive applications.
Advantages
- High surge current capability
- Low cost
- Reliable performance
Disadvantages
- Heavy and bulky
- Shorter cycle life compared to modern batteries
- Environmental concerns due to lead content
Nickel-Cadmium (NiCd) Batteries
NiCd batteries were once the standard for many rechargeable applications. They offer good performance but have primarily been replaced by newer technologies due to environmental and performance issues.
Advantages
- Robust and durable
- Performs well in extreme temperatures
Disadvantages
- Memory effect
- Toxic cadmium content
Nickel-Metal Hydride (NiMH) Batteries
NiMH batteries improved upon NiCd batteries by offering higher energy densities and being more environmentally friendly. They are commonly used in consumer electronics and hybrid vehicles.
Advantages
- Higher energy density than NiCd
- Less environmental impact
Disadvantages
- Higher self-discharge rate
- Shorter lifespan compared to Li-ion
Part 4. Applications of secondary batteries
Consumer Electronics
Secondary batteries power various consumer electronics, including smartphones, laptops, and tablets. The demand for longer battery life and faster charging times continues to drive innovation in this sector.
Electric Vehicles
Electric vehicles (EVs) rely heavily on secondary battery technology. The development of high-capacity, fast-charging batteries is essential for the widespread adoption of EVs.
Renewable Energy Storage
Secondary batteries are crucial for storing energy from renewable sources like solar and wind. They help in balancing supply and demand, ensuring a stable energy supply.
Industrial Applications
In industrial settings, secondary batteries are used for backup power, uninterruptible power supplies (UPS), and other applications requiring reliable energy storage.
Part 5. How to choose the right secondary battery?
Application Requirements
The choice of a secondary battery largely depends on its intended application. Li-ion batteries are typically preferred for high-energy applications like electric vehicles. Lead-acid batteries might be more suitable for backup power solutions due to their reliability and cost-effectiveness.
Battery Life and Performance
Consider the battery’s cycle life, energy density, and efficiency. For devices that require long-lasting power, batteries with higher energy densities and longer lifespans are ideal.
Environmental Impact
Choosing environmentally friendly battery options and ensuring proper disposal and recycling can help minimize the ecological footprint. NiMH and Li-ion batteries are generally more eco-friendly compared to NiCd batteries.
Cost Considerations
While high-performance batteries might come with a higher upfront cost, their long-term benefits often outweigh the initial investment. Evaluate the total cost of ownership, including potential savings from reduced maintenance and longer lifespan.
Part 6. Maintenance and care of secondary batteries
Proper Charging Practices
To extend the life of secondary batteries, follow proper charging practices. Avoid overcharging and deep discharging, as these can degrade the battery’s performance over time. A smart charger that automatically stops charging when the battery is complete can help.
Storage Conditions
Store batteries in a cool, dry place to prevent degradation. Avoid exposing them to extreme temperatures, which can shorten their lifespan and affect performance.
Regular Use
Regular use can maintain the performance of certain types of batteries, such as NiCd and NiMH. Periodically cycling the battery (fully discharging and then recharging) can prevent issues like the memory effect.
Safety Precautions
Always follow the manufacturer’s safety guidelines when using and handling secondary batteries. This includes avoiding physical damage, using the correct charger, and not mixing different types or brands of batteries.
Part 7. The role of secondary batteries in sustainable energy
Integration with Renewable Energy
Secondary batteries are crucial to integrating renewable energy sources into the grid. They store excess energy generated from solar panels and wind turbines, ensuring a steady supply even when the sun isn’t shining or the wind isn’t blowing.
Grid Stability and Peak Shaving
Battery storage systems help stabilize the grid by providing power during peak demand periods. This reduces the need for fossil-fuel-based peaker plants, contributing to a cleaner energy grid.
Supporting Electric Mobility
The transition to electric vehicles heavily depends on secondary battery technology advances. High-capacity, fast-charging batteries make EVs more practical and accessible, supporting the shift towards sustainable transportation.
Part 8. Future trends in secondary batteries
Solid-State Batteries
Solid-state batteries are a promising technology offering higher energy densities, improved safety, and longer lifespans than current battery technologies. They replace the liquid or gel electrolytes found in traditional batteries with solid electrolytes, reducing the risk of leaks and fires.
Advanced Materials
Researchers are exploring new materials, such as silicon anodes and lithium-sulfur chemistry, to enhance the performance of secondary batteries. These materials could significantly increase energy density and reduce costs.
Fast Charging Technologies
The demand for faster charging times is pushing the development of advanced fast-charging technologies. Innovations like ultra-fast charging stations and improved battery management systems aim to reduce charging times without compromising battery health.
Sustainable Production and Recycling
Efforts are underway to make the production and recycling of secondary batteries more sustainable. This includes developing more efficient recycling processes and reducing the reliance on rare and environmentally damaging materials.
Part 9. Conclusion
Secondary batteries are an indispensable part of our modern lives, powering everything from our gadgets to our cars. Their ability to be recharged and reused makes them a more sustainable and cost-effective choice compared to primary batteries. As technology advances, we expect even more efficient, safe, and environmentally friendly secondary batteries to emerge, driving further innovation in various fields.
Related Tags:
More Articles

LiPo Battery Discharge Rate Guide & Calculation Tips
Understand LiPo battery discharge rates, C-ratings, and how to calculate max current. Essential guide for RC, drones, and electronics users.
High‑Capacity 3S LiPo Batteries: 5000 mAh vs. 10000 mAh
Compare 3S LiPo 5000mAh vs 10000mAh batteries by weight, power, and use. Find the best fit for your drone, RC car, or boat setup.
Top 5 Applications for Small 3S LiPo Batteries
Small 3S LiPo batteries power drones, RC gear, wearables, and robotics with high energy and low weight. Making them ideal for compact electronics projects.
Building and Charging Your Own 3S LiPo Pack: A Step‑by‑Step Guide
Learn how to build, balance, and charge a 3S LiPo battery pack safely at home with this complete DIY guide for hobbyists and beginners.
How to Choose the Right LiPo Battery Plug Type?
Discover the best LiPo battery plug types, how to choose them, and expert tips for safe usage, soldering, and maintenance.